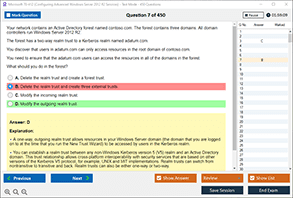
The ARP Table in a Switch: Mapping Addresses Together and Its Importance in CCNA Security Pretest Exam Answers
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table is a fundamental component of network communication, playing a critical role in ensuring that devices can communicate effectively within a network. For those preparing for the CCNA Security exam, understanding the ARP table, its functionality, and its significance is essential. This article will explore the ARP table in detail, explain how it maps two types of addresses together, and discuss its relevance to the CCNA Security Pretest Exam. Additionally, we will highlight the value of using reliable resources like Dumpsarena for exam preparation.
210-260 Exam Dumps - CCNA Security Implementing Cisco Network Security
The 210-260 (CCNA Security) exam, also known as Implementing Cisco Network Security (IINS), is a certification exam designed to validate a candidate's skills in securing Cisco networks. It is part of the Cisco Certified Network Associate Security (CCNA Security) certification track. Below are some details about the exam and the concept of exam dumps:
About the 210-260 Exam
1. Exam Code: 210-260 (IINS)
2. Exam Name: Implementing Cisco Network Security
3. Duration: 90 minutes
4. Number of Questions: 60-70 questions
5. Question Types: Multiple-choice, drag-and-drop, simulations, and simlets
6. Passing Score: The passing score is not publicly disclosed by Cisco, but it is generally around 800-850 out of 1000.
7. Exam Topics:
- Security Concepts
- Secure Access
- VPN (Virtual Private Network)
- Secure Routing and Switching
- Cisco Firewall Technologies
- IPS (Intrusion Prevention System)
- Content and Endpoint Security
Understanding the ARP Table
What is the ARP Table?
The ARP table, also known as the ARP cache, is a data structure stored in a network device, such as a switch or router. It maintains a mapping between two types of addresses:
1. IP Addresses (Logical Addresses): These are unique identifiers assigned to devices in a network, enabling communication over the internet or local networks.
2. MAC Addresses (Physical Addresses): These are hardware addresses embedded in network interface cards (NICs) and are used to identify devices at the data link layer of the OSI model.
The primary purpose of the ARP table is to resolve IP addresses to MAC addresses, ensuring that data packets are delivered to the correct device within a network.
How Does the ARP Table Work?
When a device wants to communicate with another device on the same network, it needs to know the MAC address of the destination device. Here’s how the ARP process works:
1. ARP Request: The source device sends an ARP broadcast message to all devices on the network, asking, "Who has this IP address?"
2. ARP Reply: The device with the matching IP address responds with its MAC address.
3. ARP Table Update: The source device updates its ARP table with the IP-to-MAC mapping for future reference.
This process ensures efficient communication by reducing the need for repeated ARP requests.
Mapping IP Addresses to MAC Addresses
The ARP table in a switch maps IP addresses to MAC addresses. This mapping is crucial because:
- IP Addresses are used for logical addressing and routing across networks.
- MAC Addresses are used for physical addressing and delivering data within a local network.
By maintaining this mapping, the ARP table enables switches and routers to forward data packets accurately, ensuring seamless communication between devices.
Importance of the ARP Table in Network Security
Preventing ARP Spoofing Attacks
One of the key security concerns related to the ARP table is ARP spoofing (or ARP poisoning). In this type of attack, a malicious actor sends falsified ARP messages to associate their MAC address with the IP address of a legitimate device. This allows the attacker to intercept, modify, or stop data intended for the legitimate device.
To mitigate ARP spoofing, network administrators can implement:
- Static ARP Entries: Manually configuring ARP entries to prevent unauthorized changes.
- Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI): A security feature that validates ARP packets and blocks invalid ones.
Role in Network Troubleshooting
The ARP table is also a valuable tool for network troubleshooting. By examining the ARP table, administrators can:
- Identify IP conflicts.
- Detect unauthorized devices on the network.
- Diagnose connectivity issues between devices.
The ARP Table and the CCNA Security Pretest Exam
For those preparing for the CCNA Security exam, understanding the ARP table is critical. The exam tests your knowledge of network security concepts, including:
- How ARP works.
- The role of the ARP table in network communication.
- Security measures to protect against ARP-related attacks.
Questions on the CCNA Security Pretest Exam may include:
- What does the ARP table map?
- How does ARP spoofing work, and how can it be prevented?
- What is the difference between static and dynamic ARP entries?
Having a solid grasp of these concepts will help you answer such questions confidently.
Why Choose Dumpsarena for CCNA Security Exam Preparation?
Preparing for the CCNA Security exam requires access to reliable and comprehensive study materials. Dumpsarena is a trusted platform that offers:
1. Up-to-Date Exam Dumps: Dumpsarena provides the latest exam dumps, ensuring that you are prepared for the most current version of the CCNA Security exam.
2. Detailed Explanations: Each question comes with a detailed explanation, helping you understand the underlying concepts.
3. Practice Tests: Simulate the actual exam environment with practice tests that mimic the format and difficulty level of the CCNA Security exam.
4. Expert Guidance: Access expert tips and strategies to maximize your chances of passing the exam.
By using Dumpsarena, you can streamline your preparation process and focus on mastering key topics like the ARP table and its role in network security.
Conclusion
The ARP table is a vital component of network communication, mapping IP addresses to MAC addresses to ensure efficient data delivery. For CCNA Security candidates, understanding the ARP table and its security implications is essential for passing the exam and excelling in a network security career. By leveraging resources like Dumpsarena, you can enhance your preparation and gain the confidence needed to succeed.
Whether you're exploring the intricacies of the ARP table or preparing for the CCNA Security Pretest Exam, remember that a strong foundation in networking concepts and access to reliable study materials are the keys to success. Good luck!
CCNA Security Pretest Exam Answers
9.4.2 Module Quiz – Address Resolution Answers
CCNA 1 (v5.1 + v6.0) Chapter 5 Exam Answers
CCNA 1 (v5.1 + v6.0) Practice Final Exam Answers
1. Which of the following is a primary goal of network security?
A. To increase network speed
B. To ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability
C. To reduce the cost of network equipment
D. To simplify network management
2. What is the purpose of a firewall in a network?
A. To block all incoming and outgoing traffic
B. To monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules
C. To increase network bandwidth
D. To encrypt all network traffic
3. Which protocol is commonly used to securely manage network devices?
A. HTTP
B. Telnet
C. SSH
D. FTP
4. What is the primary function of an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)?
A. To detect and block known threats in real-time
B. To encrypt network traffic
C. To monitor network performance
D. To manage user access controls
5. Which of the following is a characteristic of a strong password?
A. It is easy to remember
B. It contains at least 12 characters, including upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters
C. It is based on a dictionary word
D. It is the same as the username
6. What is the purpose of a VPN (Virtual Private Network)?
A. To increase internet speed
B. To provide a secure connection over an unsecured network
C. To block all incoming traffic
D. To monitor network traffic
7. Which of the following is a type of malware that encrypts a user's data and demands payment for the decryption key?
A. Virus
B. Worm
C. Ransomware
D. Spyware
8. What is the primary purpose of a Network Access Control (NAC) system?
A. To monitor network traffic
B. To enforce security policies on devices attempting to access the network
C. To encrypt all network traffic
D. To block all outgoing traffic
9. Which of the following is a common method for securing wireless networks?
A. WEP
B. WPA2
C. HTTP
D. FTP
10. What is the purpose of a security audit?
A. To increase network speed
B. To evaluate the effectiveness of security policies and controls
C. To block all incoming traffic
D. To encrypt all network traffic
11. Which of the following is a common type of attack that involves sending fraudulent emails to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information?
A. Phishing
B. DDoS
C. Man-in-the-middle
D. SQL injection
12. What is the primary purpose of a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) in network security?
A. To provide a secure area for internal network traffic
B. To isolate and protect external-facing services from the internal network
C. To encrypt all network traffic
D. To block all incoming traffic
13. Which of the following is a common method for detecting and preventing unauthorized access to a network?
A. Firewall
B. Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
C. VPN
D. Load balancer
14. What is the purpose of encryption in network security?
A. To increase network speed
B. To protect data by converting it into a format that is unreadable without a decryption key
C. To block all incoming traffic
D. To monitor network traffic
15. Which of the following is a common security best practice for network devices?
A. Use default usernames and passwords
B. Regularly update firmware and software
C. Disable all logging and monitoring
D. Allow all traffic by default
These questions are designed to test a range of knowledge areas relevant to the CCNA Security certification, including network security principles, technologies, and best practices.